Your cash flow can become dependent on the speed at which the retailer can sell the goods. And since you have no control over their day-to-day operations, there are no levers to pull to increase sales when you need to. SunPower has openly admitted to a material weakness in its internal control over financial reporting. In order to solve this problem, Mr. A allows the seller to put the books on their shelve without paying until they are sold. Both parties may add the additional books to prevent any shortage during the next month.
Terms Used in Consignment Accounts
The consignee now provides a summary to the consignor of all transactions it has made relating to the consignment. In this example, we will assume for simplicity the goods are sold for cash. There are often hefty maintenance charges for goods that must be incurred by the consignee and increased shipping or transportation charges that the consignor must pay. For example, when the consignee’s and consignor’s locations are far apart. As an outcome of consignment, the consignor must pay a charge to the consignee, leading to a lower revenue ratio in the consignor’s control. Indirect costs include warehouse rental, warehousing charges, advertising expenses, wages, etc.
Consignee accounts to the consignor journal entry
We’ve put this guide together to shed some light on how to account for consignment inventory, including the most important journal entries you need to know. As you might imagine, this two-way relationship can lead to complications in consignment inventory accounting. Consignment doubtful accounts and bad debt expenses occurs when goods are sent by their owner (the consignor) to an agent (the consignee), who undertakes to sell the goods. The consignor continues to own the goods until they are sold, so the goods appear as inventory in the accounting records of the consignor, not the consignee.
Inventory Observation (Objective and Explanation)
For example, you should stipulate what commission, if any, the consignee will charge the consignor and the intervals a consignee will make payments for sold inventory. Before you consider entering a consignment inventory arrangement, you should discuss and agree on the conditions. Inventory items that are sold through the consignment model are often perishable, seasonal, or previously owned. These developments underscore the potential legal and financial ramifications for the solar company as it grapples with the fallout from the alleged misreporting of crucial financial metrics. Consignment inventory is the way that consignor allows the consignee to sell the inventory without paying for it. The consignee will require to pay the consignor only when the goods are sold.
Goods Transferred by the Consignor
To completely understand consignment accounting entries, it is vital to understand the common terms used in this domain of work. Let us understand the major features of a consignment accounting entry through the detailed explanation below. The consignee also has the option to return any unsold or damaged goods to the consigner. Other names used for consignment inventory are consignment goods or consignment sales. Consignment accounting balance signifies profit or loss upon consignment and is moved to the “Profit & Loss section in Consignment Account.” As a result, the consignment profile is closed.
Try Unleashed for free today or book a demo to learn how we can help your business make light work of consignment inventory accounting and stock management. Unleashed inventory management software gives retailers, wholesalers, and their suppliers the ability to track stock across multiple warehouses and geographical locations. Plus, you can easily integrate it with all your existing business software for a fully connected system that updates itself in real-time.
- To ensure maximum accuracy and profitability when dealing with consignment stock, you’ll need a robust inventory management system.
- This journal entry indicates the transfer of inventory from the standard inventory account to a separate consignment inventory account.
- So entire profit or loss belongs to the consignor and consignee receives the commission as his remuneration.
- As mentioned, the consignor must use two double entries to record the transaction.
He has a CPA license in the Philippines and a BS in Accountancy graduate at Silliman University. In double-entry accounting, the shipping charges are accounted as a debit, while a credit is placed for accounts payable. You may be wondering how consignment accounting differs from traditional accounting.
As part of consignment inventory management, both parties should practice proper accounting of consigned goods. Whereas for consignees, it helps them segregate consigned goods from other inventory items. As you can see, using double-entry accounting is the easiest way to record these transactions. When you’re looking to do this in the easiest way possible, make sure that you use reliable accounting software.
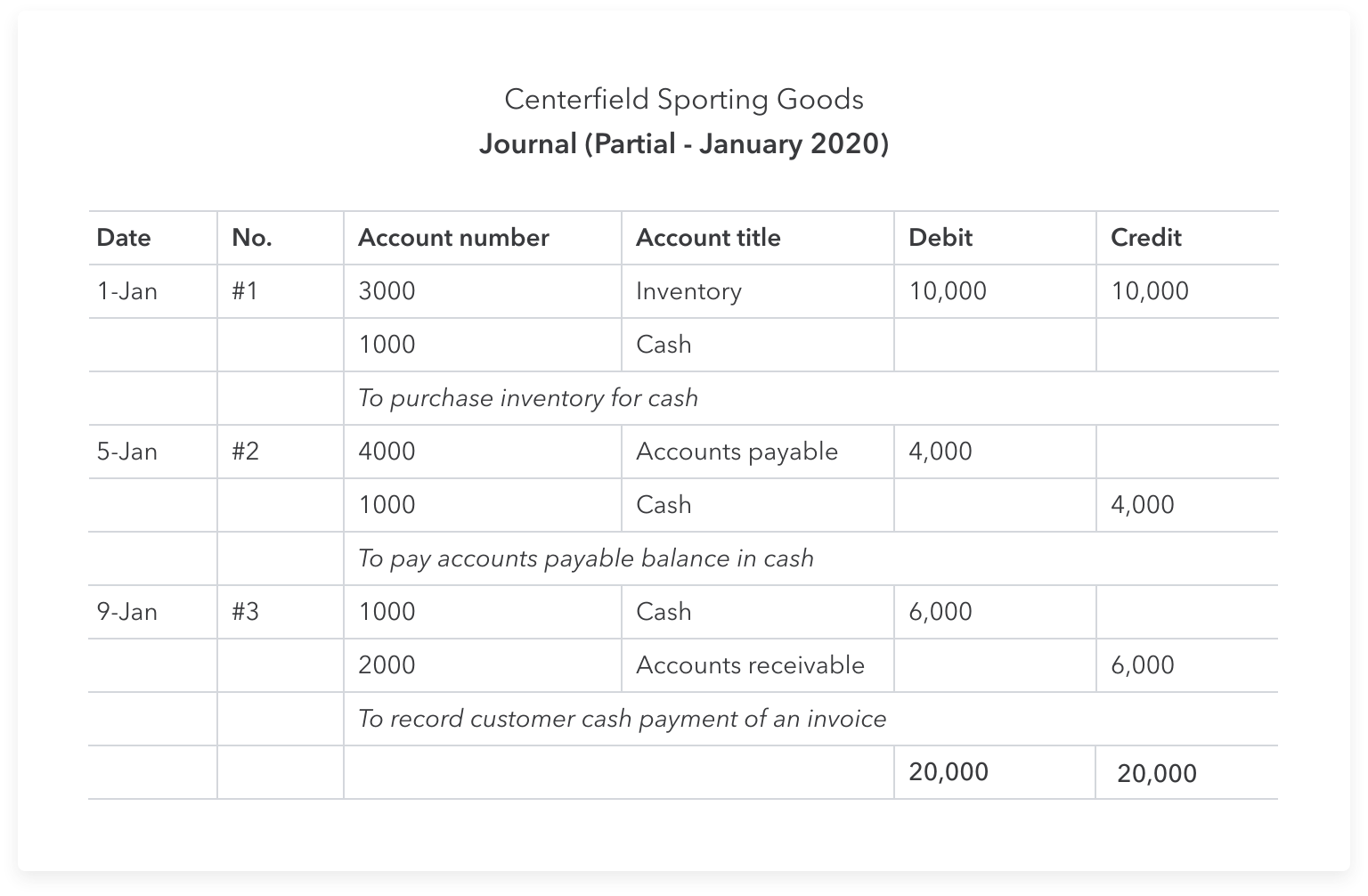
The journal entry for the consignment accounting will have a credit and a debit. It is recorded as a debit for the consignment inventory, and a credit for the store’s inventory. Below is a list of common consignment inventory accounting journal entries to help you keep correct records when selling or purchasing goods on consignment. From the consignee’s perspective, a sale transaction triggers a payment to the consignor for the consigned goods that were sold. There will also be a sale transaction to record the sale of goods to the third party, which is a debit to cash or accounts receivable and a credit to sales. In case the consignee returns unsold goods, the consignor doesn’t need any accounting entries.
Any expenses incurred by the consignee in connection with the consignment are reimbursed to him. Most often he deducts these expenses from sale proceeds along with his earned commission. This details revenue and expenses incurred on the sale of the goods. When the consignee sells the goods, they’ll give the consignor’s account a credit. To ensure maximum accuracy and profitability when dealing with consignment stock, you’ll need a robust inventory management system. As the inventory has now been sold, the consignee provides an account summary to the consignor.